Nothing says that you are committed to renewable energy and the environment like owning or replacing your petrol/diesel car with an electric car.
To halt climate change and save the world, the transition to sustainable mobility and transport electrification is essential. Electric vehicles will replace those with combustion engines in the medium term, a move that involves research and development of more reliable, powerful electric batteries, the cornerstone of these vehicles, which must be environmentally friendlier as well.
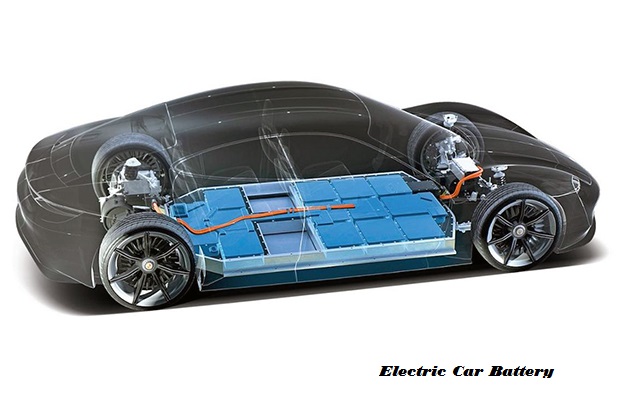
How does the Electric Car Battery work?
The batteries used in Electric Cars are Lithium-ion. Lithium-ion batteries were first produced for commercial purposes, i.e., for the consumer electronic sector. For all devices needing a portable rechargeable battery, it soon added itself to more applications, eventually becoming easily available. Nickel-cadmium (NiCd) and nickel-metal hydride (Ni-MH) technologies have been substituted by Lithium-ion.
The idea behind the lithium-ion battery is to circulate electrons by generating a difference in potential between two electrodes that are submerged in a conductive ionic liquid called the electrolyte, one negative and the other positive. Through the discharge process, the electrons stored in the negative electrode are released by an external circuit to travel to the positive electrode while the battery is powering a device. On the other hand, the energy provided by the charger sends the electrons back from the positive electrode to the negative while the battery is charging.
In easy terms, an electric car battery accumulates the energy that stores electricity for an alternating or continuous current engine to be transmitted. Its relevance, however, is much greater than this. What makes these vehicles sustainable is the battery that releases them from their reliance on fossil fuels. Batteries are the heart of the concerns of the buyers because they determine the range of the car, the distance a vehicle can travel before a charge is required, its charging time, and its price.
Who are the manufacturers of Electric Car Batteries?
A significant number of manufacturers of electric car batteries exist. Some are well-known, such as Tesla and Nissan, while others, such as BYD or LG Chem, may not be as well-known around the world, but they are still important players in the production of electric car batteries. For eg, LG Chem supplies the likes of Volvo, Renault, Ford, and Chevrolet with electric vehicle batteries. In addition to this, they also signed an agreement with Telsa for the supply of batteries to all Telsa manufactured in China.
How cost-efficient are the Electric Car Batteries?
As stated by BloombergNEF in 2019, if we concentrate uniquely on the price of a battery following its power capacity, we should expect a purchase price of around 140 Eur/kWh and not forget that these purchase prices are falling year after year. So, depending on the country, a Renault ZOE 52 kW/h electric battery alone is priced at around 8,100 euros.
Moreover, for at least 1,000 full-charge cycles, vehicle batteries are typically designed to retain maximum performance. But their lifetime goes way beyond that, which provides significant assurance of efficiency. When you purchase a battery, for example, Renault promises it for 8 years (or 160,000 kilometers).
Although an electric car’s initial price might be higher than that of a combustion engine car of a similar class, driving it will cost half as much per mile. For an oil change or a filter, spark plug, or timing belt replacement, an electric motor would never need to be swallowed. There’s a lot less load on the brake pads and brake disks, due to regenerative braking. Plus, even more, manageable is the electricity prices.
What are the specifications of the Electric Car Batteries?
Efficiency – The battery capacity, i.e. the percentage of energy that it is capable of providing about the energy that is put into the process of charging.
Voltage – The power per kilogram of weight of the battery that the battery can supply, which is therefore expressed as W/kg (Watts per kg). The larger the power, the greater the vehicle’s efficiency.
Life Cycle – The number of times a battery can be charged and depleted, as they lose power, before requiring replacement. The more cycles there are for the battery, the longer it will last.
Charging Speed – There are three forms to charge an electric car battery, with times varying according to the car model: quick (10-40 minutes), fast (1.5-3 hours), and slow(5-8 hours).
Conclusion
Batteries are constantly innovating. Swiss start-up Innolith AG recently revealed that it had built a denser battery capable of storing more energy and growing the range to up to 1,000 km, without increasing weight or height. The secret being lithium batteries with electrolytes that are not flammable.
Electrolyte-based solid-state batteries may also be placed at the forefront of the sector because they are cheaper, lighter, and smaller, improve energy density, and do not require heating prevention protection systems.