
The term used to define the increasing number of safety features designed to increase the safety of drivers, passengers, and pedestrians by reducing the severity and the total number of motor vehicle accidents is Advanced Driver Assistance System or ADAS.
To prevent an accident, the Advanced Driver Assistance System “ADAS” may warn drivers of possible risks, intervene to help the driver stay in control and, if necessary, minimize the impact of an accident if it cannot be prevented. In short, our errors are compensated by ADAS, whether they are inattentiveness, incorrect control inputs, or, to a degree, downright stupidity.
The umbrella under which ADAS resides has grown larger and larger as the related ADAS technologies are built and refined, and car manufacturers aim to attract consumers with a growing variety of safety and convenience-focused features.
The word Advanced Driver Assistance System “ADAS” now encompasses an increasingly large and increasingly widespread range of passive and active systems, offered as an alternative or as a standard for a growing number of new cars and commercial vehicles. Some ADAS functions are so well established and productive that in some regions across the globe they have become compulsory.
Table of Contents
Famous ADAS In Today’s Cars
You’ve seen the advancement of in-car technology if you’ve been shopping for a car in the past few years. New features have first emerged as premium safety and convenience options, then as driver-assist and safety systems for standard equipment. These Advanced Driver Assist Systems “ADAS” are designed to automate an increasing number of processes in vehicles to reduce the driver’s manual interaction.
Active Park Assist
- Active Park Assist helps the driver to complete a parking maneuver, otherwise known as Intelligent Parking Assist. In some vehicles, for parallel and perpendicular parking, the system takes over steering control while the driver operates the gearshift, accelerator, and brakes.
- The system performs the full parking process for other systems, such as Ford’s Enhanced Active Park Assist, while holding down a single button.
- Parking spots appropriate for your vehicle can even be identified by the system.
- The days are over when you need to drive up and down crowded parking lots in search of a free place.
Adaptive Cruise Control
- Adaptive Cruise Control also referred to as Distance Control, uses forward-viewing cameras, LiDAR, and sensors when cruise control is set to maintain a safe following distance from vehicles ahead in traffic.
- The maximum set cruising speed is retained when the way ahead is clear, but when a vehicle appears ahead of your car, the vehicle will automatically slow its speed.
- Stop-and-Go, safely bringing your vehicle to a complete stop, and resuming travel with little to no driver input are many adaptive cruise control systems.
Adaptive Front Lighting System
- The Adaptive Front Lighting System increases on-road visibility at night on some premium models.
- To coincide with the direction you point your vehicle, the system uses steering input to turn headlight beams.
- AFLS on-road curves can help drivers identify obstacles earlier on the road to prevent hazardous maneuvers and accidents.
Automatic Emergency Braking
- Forward-viewing cameras and radar sensors determine when the road ahead is an obstacle or a vehicle. In some instances, systems detect pedestrians as well.
- Automatic Emergency Braking brakes are applied automatically to prevent or mitigate the severity of an impact if the system detects an obstacle and there is no driver input to prevent the collision.
Lane-Departure Warning System
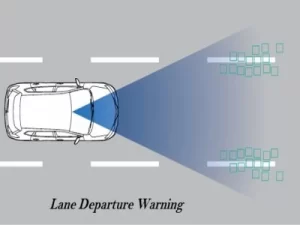
- LDWS is a device that allows drivers to maintain the line of their vehicle when on the highway, another simple but successful function on the market today.
- In other words, the sensors and cameras mounted on the vehicle can assess whether or not the driver is weaving in and out of his lane without the use of signs for the turn signal.
- If it detects weaving moments, the car will reply with different beeps to get the attention of the driver and thus maintain the line at all times.
Driver Attention Alert
- For those that travel regularly, this function will come in handy. DAA is crucial in holding your focus on point while you’re on the lane, whether it’s for long highway drives or even long-term city driving.
- Imagine driving on a single ride for more than six hours and you’re feeling drowsy. By flashing a sequence of warning signs to the driver, DAA helps to regain the driver’s attention. Both in audible forms, such as beeps and bongs, or via a visual aid. For instance, with its DAA system, Proton has a simple but effective process.
- It depicts a basic picture of a coffee cup as well as a “Take a break” message located below.
Drawbacks Of Advanced Driver Assistance System ADAS
Now, it is important to have characteristics such as those described above and can help minimize the number of possible incidents, but it does have its disadvantages, however. There are a few here worth remembering. Having a plethora of technical advances, for example, means we’re moving into a new and dangerous technological age.
- With the safety technology suite installed into a car, this may also imply that drivers will acquire the mentality of “have nothing to fear,” which could contribute to disdain towards other road users. Features such as Blind-Spot Monitoring (BSM), both active and passive reversing cameras, and even driven parking systems can make new drivers complacent while driving.
- This brings up another topic at hand, as well. At present, Malaysia has no regulation of insurance laws to tie in with the Advanced Driver Assist System as of now. In other words, there will be no special provision to excuse the crash at all, regardless of whether your vehicle has the active safety suite and you’re involved in an accident.
- The cost of repairing missing or damaged parts that can cost upwards of RM1000 depending on the amount of technology affected is another setback. Our country is still undergoing its testing process, whatever it may be. In addition to that, in general, Malaysians are more comfortable buying cheaper cars with lower protection and safety considerations for themselves and those around them.
Conclusion
Seeing that Advanced Driver Assist System is becoming increasingly prevalent in new cars, to the point that a feature that was once so unique in the category of luxury and upmarket cars are now trickling down to the cheapest cars such as the Perodua Axia and Kia Picanto, it is safe to say that in the automotive world this safety suite is certainly on the right road.





